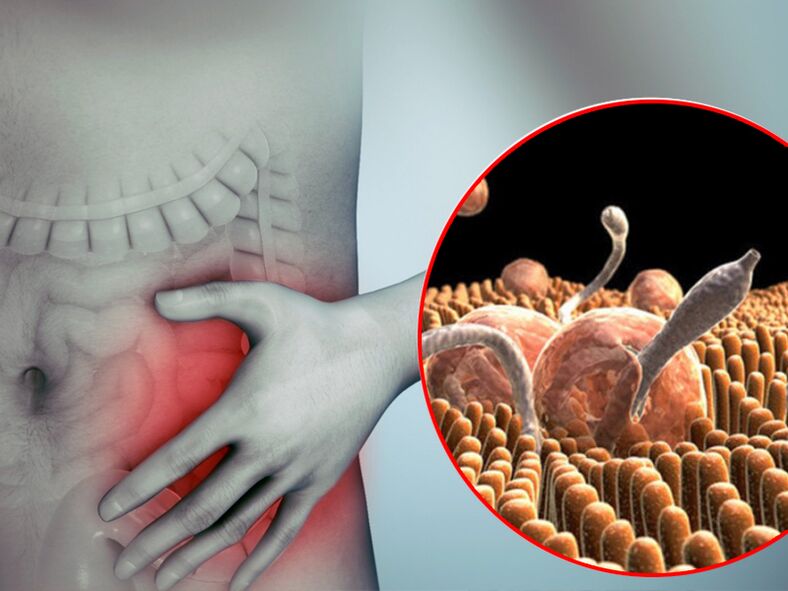
Parasites can settle in the human body, any of its organs and systems. These creatures enter the body from the environment and multiply throughout the body with blood flow. There are many types of parasites that can settle in the human body. Each poses a threat to human health and causes negative changes in the way organs work. So today we are going to talk about the types of human parasites. In the following article, you can find out which parasites can settle in the human body.
How to get infected with worms
To protect yourself, you need to know 4 ways to spread and infect worm eggs with eggs:
- Through soil and water - geohelminthiasis. They develop in sand, soil and water, then enter the human body and start laying eggs there. Furthermore, the worm’s egg, along with the feces, enters the outside environment and waits in the wings to infect a new person. Consuming poorly washed vegetables and fruits, dirty hands, dust on food can lead to infection with human geohelmet samples. Some parasite eggs enter the human body through the skin of the feet and ankles.
- Through a direct connection. Worms that occur in pets and humans are spread through manual contact, play, and common activities.
- Through the use of contaminated food of animal origin - biohelminthiasis. Consumption of raw and poorly processed meat (kebabs, bacon, compotes, homemade game) and fish (sushi, dried fish, canned fish) is potentially dangerous. There is a possibility of intestinal infections and the capture of biohelm samples.
- With insect bites. This type of infection is quite rare. These include intestinal myiasis, cantariasis and scoleciasis. Do not mix parasitic eggs and insect larvae that deposit under the skin of animals and humans (for example, fly larvae).
The main mechanisms of worm spread
- Soil, sand and other types of soils are the most fertile habitats for worm eggs. Growing plants are in constant contact with the soil. During the harvest, the greens, fruits and vegetables come into contact with the hands of the workers, the dusty shelves of the grocery stores, and the trucks. Under these conditions, there is a high probability of food contamination with parasitic eggs. Therefore, products of plant origin should be washed thoroughly under running water and then rinsed with boiling water. You need to be especially vigilant in the countryside, where pets walk around the yard and then go into the house. It’s not hard to imagine what kind of sewage a cat or dog can bring into the house after an overnight walk. Flies and cockroaches are also carriers of helminths. When you sit on food, insects can infect the food. Any contact with soil and sand can lead to parasites entering the human body. Therefore, it is necessary to wash your hands thoroughly, especially under the nails. This is especially true for children.
- From person to person. This infection mechanism is extremely effective. For example, pinworms lay eggs around the anus at night. A sleeping child scratches the egg-laying site as itching begins there. Thousands of eggs fall on the clothes, on the bed, and in the morning on the handles and everything a little guy touches in the morning before washing their hands and washing their face. As a result, the entire family is at risk of infection.
- In contact with water. Open water bodies contain a huge number of worms. There is a serious risk of infection from bathing and accidental ingestion of water
Children are much more likely to be exposed to helminthic invasion than adults. This is due to the fact that the child’s body is poorly protected (defense mechanisms are still evolving) and the child is actively in contact with the external environment. It takes an incredible effort from her parents to teach her the basic rules of personal hygiene. Children are much more likely to be exposed to helminthic invasion than adults.
Infants under 6 years of age are at high risk of infection. According to statistics, about 95% of children under the age of 4-5 are infected with worms. Therefore, special attention should be paid to prevention. Most worms are found in the body, they only lay down there and after a certain time they die. For example, pinworms live for 6-8 weeks, wheelworms - up to 1 year. The number of parasites in the body only increases with the penetration of new eggs from the outside.
The treatment allows you to get rid of worms much faster and stop laying eggs in the intestines. Cure for children with helminthic infections is almost impossible without medication. New eggs are constantly entering the oral cavity, filling the line of adults in the child’s body.
What are the signs of helminthic invasion recognition
The signs of the appearance of worms in humans are obvious and hidden. The obvious ones include "unreasonable" weight loss, a pale appearance (anemia of the skin), chronic fatigue, and itching at night in the anal canal. These manifestations are well known and suggest contamination.
It is not uncommon for helminthic invasion, in which diseases of the internal organs are exacerbated, diseases that have not occurred before. These are considered hidden signs. People are taken to treat many diseases and the cause is ignored. However, therapy does not work. Here are some examples:
Infectious diseases due to decreased immunity
Parasites consume many nutrients and release toxic substances in the human body. Such conditions significantly reduce the patient's immunity. Exacerbation of chronic diseases and various inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx may begin. Treatment of sinusitis or stomatitis in the usual way is pointless. It is important to rule out the cause. Inflammation of the uterine appendage, vulvovaginitis, and vaginosis of various origins can often begin in girls and women.
General malaise due to intoxication of the body
The more severe the intestinal worm invasion in the patient, the more harmful substances the parasites emit. This has a detrimental effect on the well-being and nervous system of adults and children. Examples are migraine, dizziness, joint pain. After overcoming nausea, he takes painkillers, but the pain returns soon: the cause of the disease has been ignored. The more severe the invasion of the intestinal worm in the patient, the more harmful substances are released by the parasites
In children, nervous system disorders are accompanied by irritability, apathy, and aggression. If your child is sleeping poorly, talking in a dream, having nightmares, or slipping into school, it’s time to start preventing helminthiasis.
Allergic reactions, skin pathologies
The waste products of worms are perceived as triggers of allergens. Skin reactions (rash, itching, rash, peeling) are the minimum number of symptoms that occur at the onset of allergy. General reactions of the body are likely: worsening of asthma, runny nose, cough. Sometimes the helminthic invasion is accompanied by fragility and hair loss, cracking of the skin of the corners, and peeling of the nails.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Depending on the severity of the infection, symptoms can range from mild to severe. From mild nausea and diarrhea to chronic bloating, constipation, vomiting, umbilical cord and hypochondria pain. Worms in tissues do not affect the gastrointestinal tract as much as intestinal parasites.
What organs can parasites live in?
Worm parasites are classified into two categories that correspond to the site of activity in the donor’s body.
- Cavity - worms that live in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract. There are about 100 species of intestinal parasites, and there are one to two dozen species in each section of the intestine. The small intestine is ready to accommodate the roundworm, antilostomy, broad tapeworms, and other less common "siblings. "The small intestine "shares habitat" with dumplings, dwarf tapeworms, and others. The medical literature describes cases where a person is infected with several types of parasites at the same time.
- Tissues - worms localized in organs, tissues and even the blood. Modern medicine successfully copes with paragonimiasis (lung), cysticercosis (brain), echinococcosis (liver) and filariasis (lymphatic). The larvae of some worms move through the circulatory system throughout the body and are randomly attached to any organ. If a lot of eggs get in, the whole body can become infected.
Symptoms of worms depending on the type of parasite
The symptoms of different types of worms that occur in humans can be different. It is also worth considering the duration and severity of infection with the parasites, as well as the patient's general condition prior to infection. The table below summarizes the main symptoms of the presence of worms in humans by their type.
| Type of parasite (disease) | Method of infection | Symptoms | Time of onset of symptoms |
| Pinworms (enterobiasis) | With food of plant origin. | Nocturnal itching around the anus, presence of parasites in the stool, sharp, short-term pain in the navel. | 2-3 days after infection |
| Vlasoglav (trichocephalosis) | Made with unhygienic conditions with contaminated food. | Symptoms occur only in case of severe invasion: diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, appendicitis. In children, the growth of the body may be delayed and even rectal sagging may occur. | Few weeks |
| Broad diphyllobothriasis | When consuming infected river fish. | This parasite can live inside the patient for up to 25 years. Mechanical damage to the intestines, vitamin deficiency, intestinal obstruction, body poisoning, allergies. | Few weeks |
| Worm (hookworm) | When we walk barefoot on filled ground. | Itching, swelling of the feet and legs where the parasite penetrates. Cough, discharge, damage to the bronchi and lungs. Weakness, dizziness. The menstrual cycle of women is disrupted. Men have impotence. | More days |
| Ascaris (ascariasis) | With food of plant origin. | Intestinal pain, peritonitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, liver disease, pancreas. It can cause suffocation if it creeps from the gastrointestinal tract into the esophagus or airways. | About 3 months |
| Trichinella | Poorly processed meat, lard. | Nausea and heartburn, diarrhea. | 2 days |
| Liver and fascioliasis | Plant food and water. | Fever, dry cough, loss of appetite, abdominal pain. | 2-4 weeks |
The symptomatology of helminthiasis is as diverse as the pathogens of parasitosis, differing in their life cycle, intrusion pathway, migration, and favorite localization.
The general symptoms of parasitic diseases are explained by the fact that with helminthic invasions, parasites suppress a person’s own immunity, contributing to the development of inflammatory and autoimmune processes. Common symptoms are associated with poisoning, parasite death, vital activity, and proliferation, weakness, lability, and mood swings, decreased academic performance and performance, memory, and learning ability.
Pain in the right hypochondrium, the appearance of bitterness, jaundice may indicate that the parasitic disease is primarily localized in the hepatoduodenal zone (liver and duct area). However, the patient may experience nausea and regurgitation episodes (vomiting).
Symptoms associated with damage to the liver and hepatobiliary tract include, for example, infection with the flatworm, opisthorchis. This intestinal worm enters the final host, humans, through the consumption of certain types of poorly processed fish (carp). Opisthorchis
The disease is endemic and has specific areas of spread. To transmit the pathogen, the parasitic larvae have to go through a complex cycle with a host change (a mollusc belonging to a species belonging to the carp family).
It is common for many parasitic diseases to present with certain skin manifestations in the form of itchy skin, various rashes, scratches, atopic dermatitis, eczema, and the progression of other skin conditions. Dermatological processes are not always accompanied by helminthic invasion and are not successfully treated by dermatologists.
It is important that in the case of helminthiasis, any organ or tissue may be involved, patients are often worried about headaches, joint pain (joint syndrome), upper and lower respiratory complaints. Frequent cough, common ARVI, pharyngitis, laryngitis, difficulty breathing are associated with inflammation, in the infection of which infection with parasites (helminths) plays a key role.
Giardiasis and its characteristics
Giardiasis is a protozoan disease in which the pathogen exists in vegetative form and in the form of cysts. Giardia infection occurs when cysts are ingested that are very persistent in the environment and can persist in the environment for a long time (soil, food, water, various objects).
1 ml of faeces can contain millions of lamblia cysts, which can be transformed into vegetative forms if released into a favorable environment. In the human gut, cysts form a vegetative, motile form for several hours with flagella binding to the cells of the intestinal epithelium, where the pathogen finds itself in a favorable environment with the right amount of carbohydrate food and its favorite substrate. for lamblia. Giardias in a favorable environment are binary (divided into two parts) and will soon multiply in number. In addition to the intestines, the vegetative forms of lamblia also affect the hepatobiliary system (bile ducts, gallbladder).
Symptoms of giardiasis are associated with asthenia, poor academic performance, and weakness, combined with signs of damage to the intestinal and hepatic bile ducts. The course of giardiasis and other parasitic diseases is highly correlated with the characteristics of the immune response. Intestinal form, gastroenterolytic - a common form of giardiasis. The endotoxins of the pathogen may affect the nervous system, which explains the presence of many common extraintestinal symptoms.
Ascariasis
Another common and ubiquitous parasitic disease is ascariasis. This helminthiasis is more common in children, but often causes a number of complaints and symptoms in adults. Many chronic inflammatory diseases as well as somatic pathologies can start with parasite invasion and be exacerbated in the presence of various parasites (including ascaris).
Children and adults who carry ascaris often develop chronic colitis, intestinal catarrh, bronchitis, and develop serious illnesses such as bronchial asthma and other allergic processes (atopic dermatitis, eczema, rhinitis, psoriasis).
Ascaris gets into the stomach when the egg is swallowed. Upon reaching the upper part of the digestive tract (stomach), the larvae migrate from the capsule to the blood vessels, and into the alveoli of the lung system with blood flow, thereby coughing and coughing. other phenomena of bronchitis.
This condition is often considered a viral infection, an exacerbation of chronic bronchopulmonary disease, and in this case is usually associated with the movement of parasitic larvae.
After coughing up the ascaris larvae and entering the pathogen with secretions, they are ingested with saliva and returned to the stomach, where they have favorable conditions for further growth and development of the parasite. After coughing up the ascaris larvae and ingesting the pathogens with secretions, they are ingested again through the saliva into the stomach and then into the intestines, where there are favorable conditions for the further growth and development of the parasite.
In the human gut, the tapeworms that feed on its contents develop into mature individuals (female 50 cm, male 20 cm). In the process of growth and activity, and as a result of the migration of larvae, the parasite has a negative toxic and mechanical effect on the human body.
In the process of growth, vital activity, laying and maturation, the pathogen suppresses the body's immunity, it can cause diseases of the lungs, intestines and other parts of the digestive system, and anemia. Ascaris can live in the human gut for up to a year.
Medicines against worms
Medical treatment of a person with tablets is possible using a number of modern devices.
Because some funds do not affect the larvae and eggs of worms and there is a high risk of re-infection (self-infection with pinworms), treatment should be repeated after 2-3 weeks. The most effective of the folk methods are the old well-established methods - the use of pumpkin seeds and tansy herb. Medical treatment of a person with tablets is possible using a number of modern devices.
The fact that pumpkin seeds are a good anthelmintic has long been known, it is best to buy unpeeled seeds, peel them by hand, preserve them and consume a thin layer of film between the seeds and the peel and consume 300 g in the morning. . within one hour, previously chopped, mixed with honey or jam. After that, do not eat for 3-4 hours and do an enema, you can repeat this treatment after 2 weeks.
Interesting facts about human parasites
- According to the WHO, about 3 billion people are infected with helminthic infections each year. 1. 2 billion suffer from enterobiasis, 0. 9 billion from hookworm disease, and 0. 7 billion from trichocephalosis. And that's just official stats !;
- In European countries, one in three people carry intestinal parasites in their body;
- In severe invasions, a person loses up to 500 ml of blood per day. Hence diseases and chronic fatigue;
- Some parasites are localized in the brain, eyeball, and bone marrow and can live there for up to 30 years. For example, cytisterk. ;
- Females in Ascaris lay 240, 000 eggs a day. Constant re-infection does not allow a person to recover for the first time. Repeated treatments are required;
- The waste products of parasites - poisons and toxins - undermine human health 24 hours a day;
- Some types of tapeworms reach 12 meters in length. Sometimes it threatens human intestinal obstruction;
- Pumpkin seeds contain cucurbitin, which helps cure worm infections without the need for medication. Pumpkin seeds are often given to children for prevention;
- Pets are optimally treated every 3 months. This saves himself and his children from parasites;
- Wormwood can wait up to 6 months in the wings on the door handles;
- The infected dog will scatter the eggs of the parasites within 5 meters of breathing;
- In order to prevent worms and their eggs from being digested in the stomach and intestines, they release protective antienzymes;
- Trichinella does not lay eggs but produces finished worms. Therefore, it is impossible to detect the presence of this parasite under laboratory conditions;
- The most effective method for detecting invasion is the enzyme immunoassay. For tampons, stool analysis may not provide reliable information.
In summary, regular prevention of helminthic infections, even with cheap drugs (these are considered the most gentle), will help protect the entire family. Be responsible for hand and body hygiene and thoroughly prepare food for use. Children and pets need constant monitoring for the presence of parasites.